True stress and true strain pdf
2) At each True Total Strain increment, True Elastic Strain (the True Stress at that increment divided by the modulus) is subtracted off to determine the corresponding True Plastic Strain. 3) The True Total Strain at yield is equivalent to the True Elastic Strain and the True Plastic Strain at this point is zero.
engineering stress and strain values are not the true indication of material deformation characteristics. Thus the need for measures of stress and strain based on instantaneous
If the true stress, based on the actual cross-sectional area of the specimen, is used, it is found that the stress-strain curve increases continuously up to fracture. If the strain measurement is also based on instantaneous measurements, the curve, which is obtained, is known as a true-stress-true-strain curve .
We all know that the definition for strain is change is length to the original length. Now, what we mean by this original length is what sets apart the definitions of True vs. Engineering Strain. We all know that the definition for stress is load
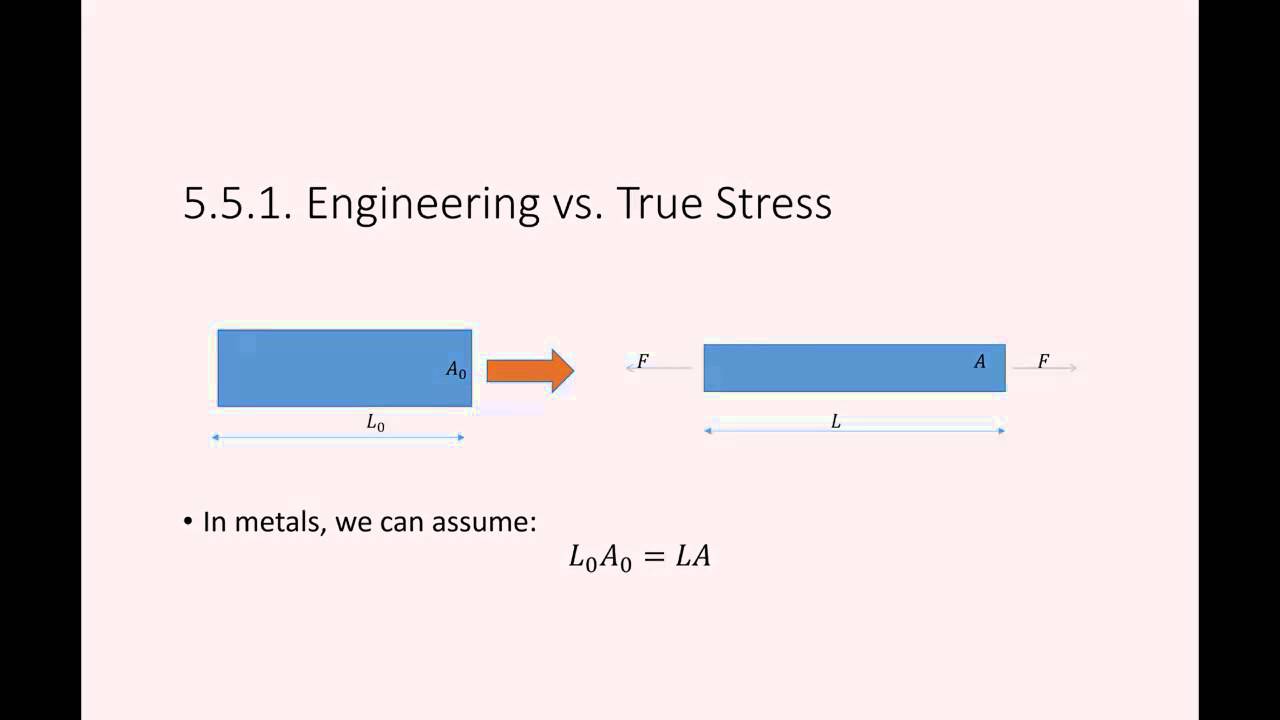
True Stress and Strain. Also see Engineering Stress and Strain. True Stress. The true stress (ø) uses the instantaneous or actual area of the specimen at any given point, as opposed to the original area used in the engineering values.
Engineering Stress –Engineering Strain Load applied acts over an area. Parameter that characterizes the load effect is given as load divided by original area over which the load acts.
True Stress / True Strain. To request a quotation for any test email info@trl.com for a prompt reply. Whereas engineering stress is based on the original dimensions of a specimen, the true stress is based on an instantaneous measurement of the cross-sectional area.
THE TRUE STRESS-TRUE STRAIN RELATIONSHIP 21 3 s = F/A, (1) e = (I – lo)/lo where A, and I, are the cross-sectional area and the length of the original,
effective plastic strain (input value) = total true strain – true stress/E Note that as the stress value increases, the recoverable strain ( true stress/E ) increases as well. For metals, E is very large compared to the yield stress so it’s fairly common practice in the case of metals to just subtract off a constant value equal to the strain at initial yield from all subsequent strain values.
materials Why do we even use engineering stress

Stress-Strain Concepts Revisited – Part 2 materion.com
True Stress – True Strain Curve. W skrócie: The engineering stress-strain curve does not give a true indication of the deformation characteristics of a metal because it is based entirely on the original dimensions of the specimen, and these dimensions change continuously during the test.
Uniaxial True Stress-Strain. after Necking Yun Ling AMP Incorporated ABSTRACT A weighted-average method for determining uniaxial, true tensile stress vs. strain relation after necking is
Stress-Strain Concepts Revisited – Part 2 Last month’s edition of Technical Tidbits started to explore the concepts of properties that can be obtained from a material’s stress-strain curve. This is a continuation of that discussion. basics with an in. After the yield strength is exceeded, the stress-strain curve continues to rise to a maximum point known as the . tensile strength. or the
true stress-strain curve, the stress will continue to increase to failure. However, unless the minimum cross- However, unless the minimum cross- sectional area is continuously measured so that the true strain can be accurately calculated, the calculated

10/10/2008 · I recently read the thread Nonlinear FEA with Von Misses Plasticity in 17-4 PH900 Stainless Steel and have a question about the original poster’s use of the ‘true stress’ vs. ‘true strain’.
artificiality of the engineering stress versus true stress approach. Occasionally, the end of the straight line portion of the curve is difficult to identify and so we use a graphical means to define it.
True stress (·)true strain (¾) relationships until just before fracture, i.e., the plastic deformation limit, were estimated by the stepwise tensile test and the Bridgman equation for various metals and alloys with different crystal structures.
Modeling continuous shape-forming processes such as rolling, drawing, extruding, etc. requires a deep understanding of the mechanics of plastic deformation to perform successfully, and to that end true stress and true strain are invaluable.
Unless thickness and width are being monitored continuously during the test, you can not calculate true stress. it is, however, a much better representation of how the material behaves as it is being deformed, which explains its use in forming simulations. in circle grid analysis, engineering strain is the% expansion of the circle compared to the initial diameter of the circle. The
Before starting with the FE analysis, material input is developed in terms of true stress strain relation. These material input are created for each material (for base and weld material). Provided with these

True Stress Calculation Given below is the true stress strain calculator to know the determination of the load acting on the instantaneous cross-sectional area. True stress is the applied load divided by the cross-sectional area of the specimen at that load.
12/06/2015 · In this video I introduce true stress and true strain which we can then use in the strain hardening equation to quantify the relationship between the load and the resulting elongation in a sample
true stress–strain relations in the post-uniform elongation range through an inverse analysis by FEM, on the basis of measured change of n-value with strain in the uniform
13/06/2016 · Get YouTube without the ads. Working… No thanks 3 months free. Find out why Close. Mechanisms of Deformation & True Stress-Strain MELearn – UTRGV Ley. Loading… Unsubscribe from MELearn – UTRGV
the relevant stress and strain measures. As had been shown by Ji, Waas and Bazant [2], the use of non-conjugate As had been shown by Ji, Waas and Bazant [2], the use of non-conjugate stress and strain increments in finite element programs can cause errors as large as 100%.
True Stress & True Strain Engineering Stress-Strain
iii ABSTRACT IVÁN DARÍO ROMERO FONSECA. Correction of the post-necking True Stress-Strain data using instrumented nanoindentation. (Under the direction of DR.
Video created by Georgia Institute of Technology for the course “Mechanics of Materials I: Fundamentals of Stress & Strain and Axial Loading”. In this section, we will study the fundamentals of stress and strain as applied to Mechanics of
The corresponding true stress and the true strain, which recognize the deformed geometrics of the section during tests, can be established directly from the engineering stress and the engineering strain based on the concept of uniform stress, small dimensional change, and incompressible material, which is valid for steel. – serie true blood tome 13 pdf Deformation in continuum mechanics is the transformation of a body from a reference configuration to a current configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body.
beyond recovery—at an engineering strain of 0.002, or 0.2%. At this value, the difference At this value, the difference between engineering and true strain is less than one part in a thousand.
In a tension test, true strain is less than engineering strain. Thus, a point defining true stress-strain curve is displaced upwards and to the left to define the equivalent engineering stress-strain curve. The difference between the true and engineering stresses and strains will increase with plastic deformation. At low strains (such as elastic deformation), the differences between the two is
The true stress at fracture can only be measured by actually carrying out an experiment and measuring the deformation. That is why it is the true stress, because it is what literally happens.
In practice, it is noteworthy to mention that the true stress and strain are basically indistinguishable from the engineering stress and strain at small deformations (Figure 8). Yet, it should be noted that the true stress could be much larger than the engineering stress once the strain increases and the consequently, the cross sectional of the specimen decreases.
The true stress-true strain model parameters were established through matching of numerical analysis results with the corresponding standard uniaxial tensile test experimental results. The
Engineering stress and engineering strain are computed using the original specimen dimensions. OPTI 222 Mechanical Design in Optical Engineering 19 Ductile Material Test Specimen True stress and true strain are based upon instantaneous values of cross
In Abaqus (as in most fea software) the relevant stress-strain data must be input as true stress and true strain data (correlating the current deformed state of the material with the history of previously performed states and not initial undeformed ones).
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE36(2001)3119– 3128 Drawability and attainable mechanical properties of polyamide yarn using true stress–true strain curves
nonzero normal stress sx 5s, sy 5sz 5txy 5tyz 5tzx 5 0. (9) If the material is isotropic, which shall be assumed throughout this paper, the strains in the uniaxial state are:
At any load, the true stress is the load divided by the cross-sectional area at that instant. Unless thickness and width are being monitored continuously during the test, you cannot calculate true stress. It is, however, a much better representation of how the material behaves as it is being deformed, which explains its use in forming simulations. In circle grid analysis, engineering strain is
KL Murty page 2 MAT 450 Stress – Strain Curve Definitions Nominal (engineering) vs True S = P Ao, e = ∆l lo σ = P A , ε = ln (l lo) Proportional limit (PL)
18/11/2008 · Best Answer: enginnering stress is Force / prime (early) Area = F/A0 True stress is Force / Area in any time = F/A engineering strain is (Lf-L0)/L0 while Lf is lenght of sample after deformation and L0 is early lenght of sample (before deformation)
True Strain Calculator Easycalculation.com
definition of true strain : after a load P is applied to the specimen, the length changes from L 0 to L , an additional load dP produces an incremental length change dL , the strain de due to
This is a plot of true stress versus true plastic strain, which is sampled to reduce the number of data points and then used in tabular form within elastic-plastic materials models. More information on the
True Stress (σ T) True stress is the stress determined by the instantaneous load acting on the instantaneous cross-sectional area True stress is related to engineering stress:
Estimations of the True Stress and True Strain until just

True stress true strain and work hardening YouTube
The true stress would be 20% higher in the case above where the specimen is 20% longer than the original length. As the relative elongation increases, the true strain will become
Corrected True Stress – True Strain Curv – Download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online.
This gives a true strain result that is in the initial reference orientation, like a Green strain tensor. The result is a bit of a hybrid because it is based on ({bf D}), which is clearly an Eulerian quantity, but it is in the reference orientation, like a Lagrangian quantity. Granted, it also requires a
True stress 1. True Stress – True Strain Curve: Part One Abstract: During stress testing of a material sample, the stress–strain curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress, obtained from measuring the load applied on the sample, and strain, derived from measuring the deformation of the sample.
The true stress- true strain response of nitrogen alloyed austenitic manganese steel with chromium additions in the as-cast and heat treated conditions under compression loading was also studied.
white paper Influence of chromium additions and true

Engineering Stress True Stress materion.com
Abstract. Average true flow stress-logarithmic true strain curves can be usually obtained from a tensile test. After the onset of necking, the average true flow stress-logarithmic true strain data from a tensile specimen with round cross section should be modified by …
strain, engineering stress, true strain, true stress. Fill in for the eight points on graph. Fill in for the eight points on graph. What is the percentage difference between true …
1 HyperMath – Calculate true stress and strain from engineering stress and strain experimental data The true strain ( ) and true stress ( ) are defined by the following equations:
True stress and Engineering stresses are a bit different. Consider the figure showing stress-strain relationships of a mid-steel. **image source-R.C.Hibbeler-Mechanics of Materials 8th Edition The above figures are the stress vs. strain graph of a…
Average true flow stress-logarithmic true strain curves can be usually obtained from a tensile test. After the onset of After the onset of necking, the average true flow stress-logarithmic true strain data from a tensile specimen with round cross section
Correlation between Engineering Stress-Strain and True
Relation between True stress and Engineering stress When a ductile material is subjected to tensile stress, beyond a certain stress, the cross sectional area of the material decreases at a particular position in the material; i.e. a construction develops at a particular position.
PDF The most commonly accepted method in evaluation of the mechanical properties of metals would be the tension test. Its main objective would be to determine the properties relevant to the
= (1+ ) , where is the engineering stress and is the engineering strain (Equation 6.18a) Equation 6.18a is invalid once necking begins.Hence, the values of the measured diameter of the specimen given in the question are to be used to calculate true stress, for the last four data points.
The true stress (σ)–true strain (ε) relationships up to the plastic deformation limit of low-carbon ferrite–cementite (FC) steels with ferrite grain sizes between 0.5 and 34 μm were estimated at strain rates between 3.3×10 −1 and 5.0×10 −4 s −1 to investigate the effect of the strain …
CORE TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH, DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING True Stress – True Strain Analysis Summary Proper characterization of a material’s mechanical properties is critical for making

The uniaxial true stress logarithmic strain curve for a thick section can be determined from the load diameter reduction record of a round tensile specimen[ The correction of the true stress …
True stress is caused based on the original area whereas true strain is caused based on the original length. A true strain (ε t ) is a non-linear strain measurement used for large strain simulations.
– 3 – Geometric nonlinearities Engineering strain Logarithmic strain Engineering stress True stress Transformation between the stress and strain definitions
Drawability and attainable mechanical properties of
(PDF) True Stress-True Strain Models for Structural Steel
– From engineering to true strain true stress — LS-DYNA Support
Effect of strain rate on true stress–true strain


CORRECTION OF THE POST NECKING TRUE STRESS STRAIN DATA
Stress – Strain Relationships
Why are the true strain and engineering strain different
What is the difference between the true stress and the
True Stress Calculation Given below is the true stress strain calculator to know the determination of the load acting on the instantaneous cross-sectional area. True stress is the applied load divided by the cross-sectional area of the specimen at that load.
The uniaxial true stress logarithmic strain curve for a thick section can be determined from the load diameter reduction record of a round tensile specimen[ The correction of the true stress …
Relation between True stress and Engineering stress When a ductile material is subjected to tensile stress, beyond a certain stress, the cross sectional area of the material decreases at a particular position in the material; i.e. a construction develops at a particular position.
Engineering Stress –Engineering Strain Load applied acts over an area. Parameter that characterizes the load effect is given as load divided by original area over which the load acts.
PDF The most commonly accepted method in evaluation of the mechanical properties of metals would be the tension test. Its main objective would be to determine the properties relevant to the
True Stress – True Strain Curve. W skrócie: The engineering stress-strain curve does not give a true indication of the deformation characteristics of a metal because it is based entirely on the original dimensions of the specimen, and these dimensions change continuously during the test.
nonzero normal stress sx 5s, sy 5sz 5txy 5tyz 5tzx 5 0. (9) If the material is isotropic, which shall be assumed throughout this paper, the strains in the uniaxial state are:
Stress-Strain Concepts Revisited – Part 2 Last month’s edition of Technical Tidbits started to explore the concepts of properties that can be obtained from a material’s stress-strain curve. This is a continuation of that discussion. basics with an in. After the yield strength is exceeded, the stress-strain curve continues to rise to a maximum point known as the . tensile strength. or the
2) At each True Total Strain increment, True Elastic Strain (the True Stress at that increment divided by the modulus) is subtracted off to determine the corresponding True Plastic Strain. 3) The True Total Strain at yield is equivalent to the True Elastic Strain and the True Plastic Strain at this point is zero.
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE36(2001)3119– 3128 Drawability and attainable mechanical properties of polyamide yarn using true stress–true strain curves
True stress 1. True Stress – True Strain Curve: Part One Abstract: During stress testing of a material sample, the stress–strain curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress, obtained from measuring the load applied on the sample, and strain, derived from measuring the deformation of the sample.
In Abaqus (as in most fea software) the relevant stress-strain data must be input as true stress and true strain data (correlating the current deformed state of the material with the history of previously performed states and not initial undeformed ones).
We all know that the definition for strain is change is length to the original length. Now, what we mean by this original length is what sets apart the definitions of True vs. Engineering Strain. We all know that the definition for stress is load
In practice, it is noteworthy to mention that the true stress and strain are basically indistinguishable from the engineering stress and strain at small deformations (Figure 8). Yet, it should be noted that the true stress could be much larger than the engineering stress once the strain increases and the consequently, the cross sectional of the specimen decreases.
Deformation in continuum mechanics is the transformation of a body from a reference configuration to a current configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body.
True Strain Calculator Easycalculation.com
The true stress would be 20% higher in the case above where the specimen is 20% longer than the original length. As the relative elongation increases, the true strain will become
Stress-Strain Concepts Revisited – Part 2 materion.com
Deformation (mechanics) Wikipedia
– 3 – Geometric nonlinearities Engineering strain Logarithmic strain Engineering stress True stress Transformation between the stress and strain definitions
Define true stress and true strain.? Yahoo Answers
true stress–strain relations in the post-uniform elongation range through an inverse analysis by FEM, on the basis of measured change of n-value with strain in the uniform
True Stress True Strain Curve Part Two Total Materia